Research
We investigate the variability of the large-scale extratropical circulation on sub-seasonal (10 – 60 days) time scales. In the Atlantic-European region distinct weather regimes reflect the variability on these scales. Our focus is on the physical and dynamical processes driving and governing the large-scale circulation, aspects of predictability and forecast skill, and implications for surface weather.
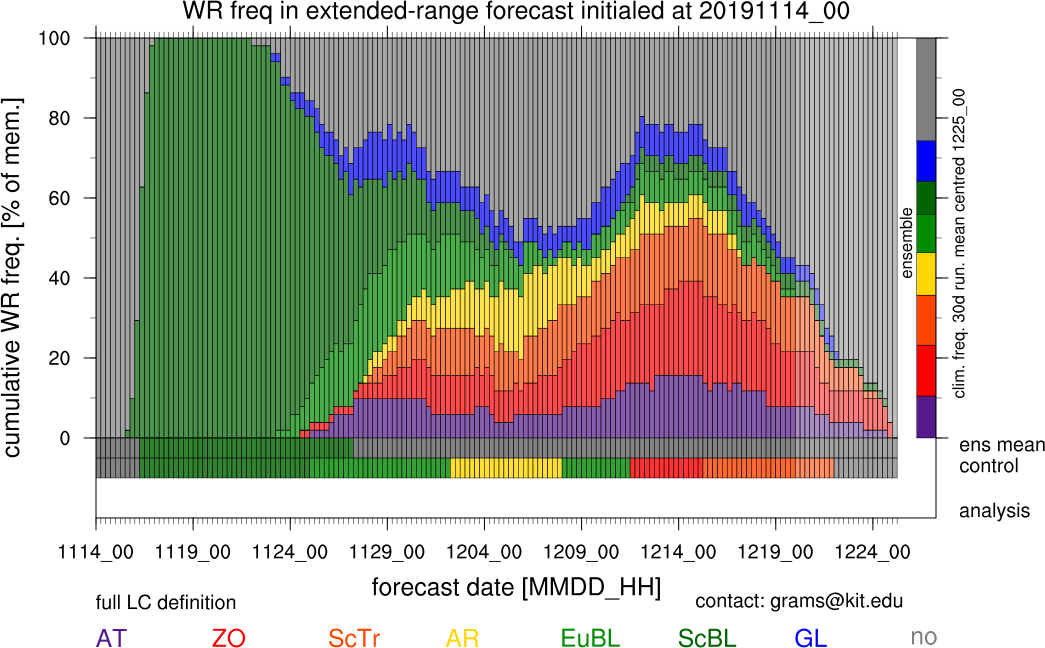
Weather regimes are persistent, quasi-stationary, and recurrent large-scale flow patterns that govern atmospheric variability of the atmosphere over continent-size regions and on time-scales of several days to a few weeks. Through imposing the character of weather for multiple days, weather regimes do not only affect our everyday life but they have major implications for various socio-economic activities, e.g. in the energy sector. Still, the correct prediction of weather regime life cycles is a major challenge for current numerical weather prediction (NWP) models.
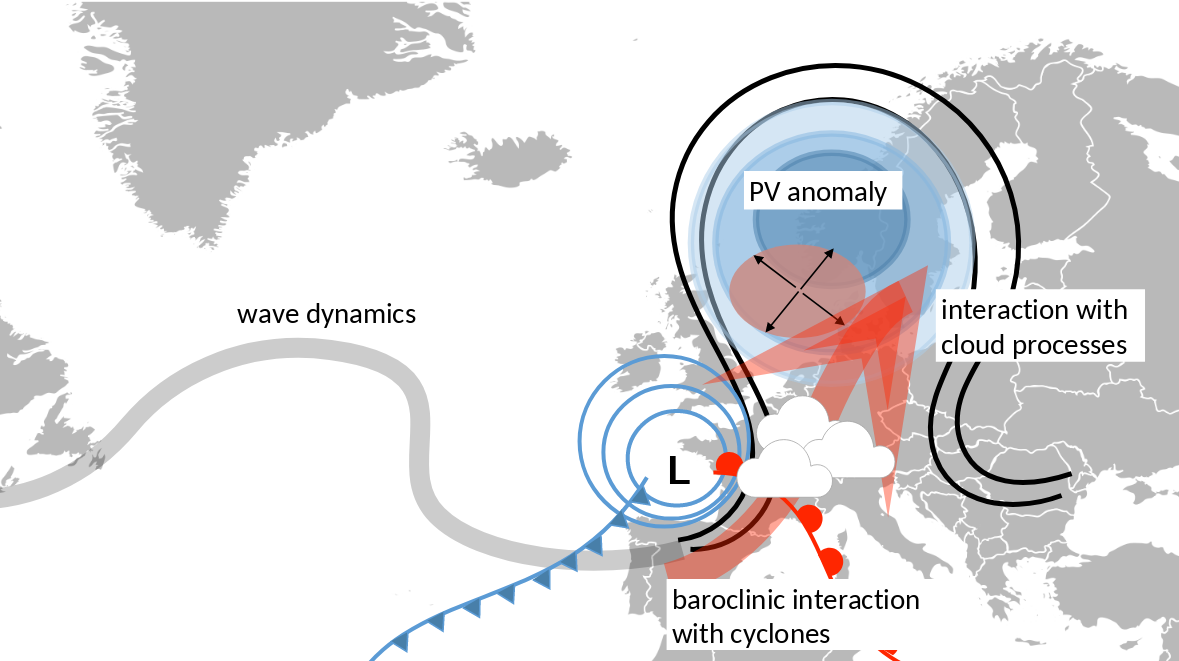
Although weather regimes govern the character of day-to-day weather, the related synoptic activity may also modulate the regimes themselves. The life cycle of blocking anticyclones, for example, is strongly modified by cloud-condensational processes related to synoptic activity. Since blocking anticyclones are a fundamental element of several Atlantic-European weather regimes, the adequate representation of midlatitude diabatic processes in NWP models is of great importance for forecasting these weather regimes.
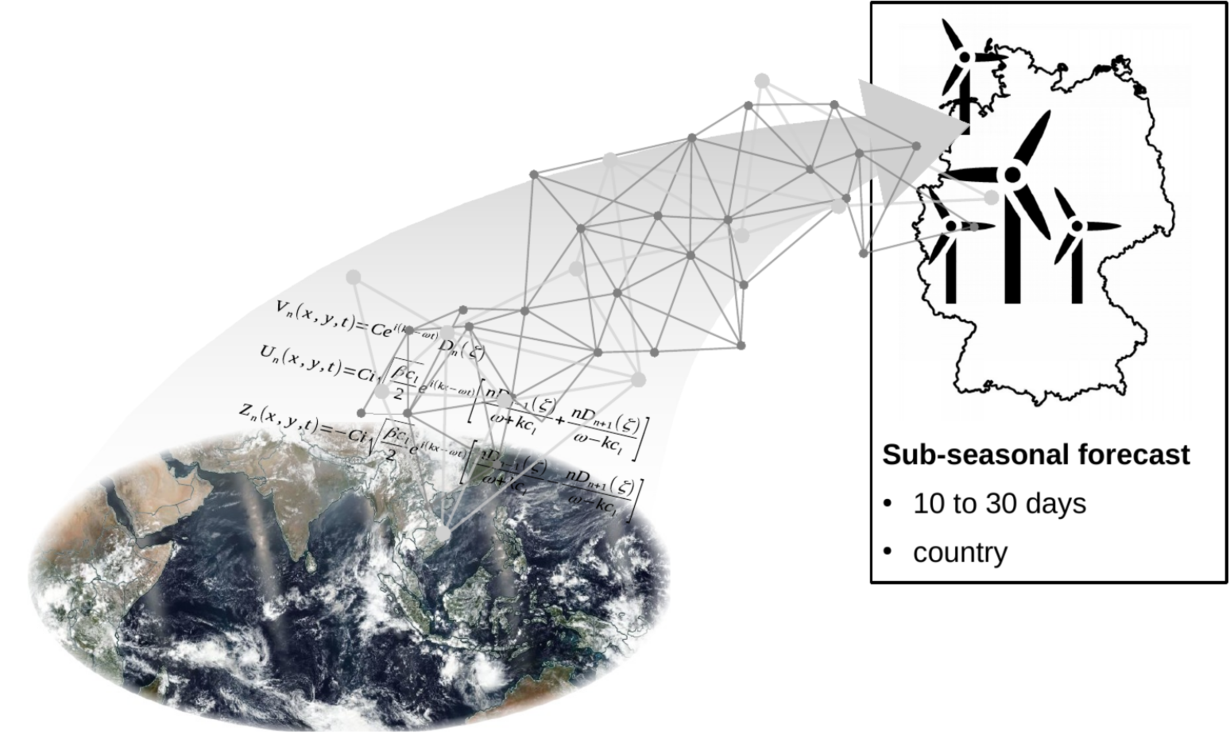
From a climate perspective, components of the climate system such as, for example, the Madden-Julian-Oscillation or the stratosphere are potential sources of sub-seasonal predictability with known impact on weather regime life cycles and synoptic activity.
By adopting an atmospheric dynamics' perspective we aim to understand how physical and dynamical processes on shorter, synoptic time scales affect predictability and forecast skill on sub-seasonal time scales and how these processes are modulated by climate modes.
Thereby we focus on the role of diabatic outflow in the life cycle of Atlantic-European weather regimes. Our applied research investigates how weather regimes affect socio-economic activities such as renewable electricity generation. We employ atmospheric reanalysis data, operational (re)forecast data from the S2S prediction project data base and sensitivity experiments with state-of-the-art global NWP models (ICON, ECMWF IFS). We further apply our diagnostic tools in real-time with operational (ensemble) forecast data. SPREADOUT is a Young Investigator Group funded by the Helmholtz Association.
Our research can be categorized into five main topics. Klick on the topics to find out more about the individual reasearch projects: